The concept of anti-correlation penalties, as described by Wahrstätter, is closely linked to the idea of countering the advantages of economies of scale.
Ethereum’s quest for decentralization has been a central theme in its evolution, with Vitalik Buterin, the platform’s creator, continually seeking innovative methods to enhance its decentralized nature. One such proposal gaining traction is the concept of anti-correlation penalties, which aims to counteract the centralizing forces of economies of scale within Ethereum’s staking ecosystem.
In a bid to enhance the decentralization of Ethereum’s staking ecosystem, Ethereum researcher Toni Wahrstätter has proposed the implementation of anti-correlation penalties. According to Wahrstätter, these penalties aim to counteract the advantages of economies of scale, which currently incentivize centralization among stakers.
Excellent work by Toni Wahrstätter, replicating and expanding on my analysis last month on cross-validator correlations and adjusting validator incentives to favor decentralization:https://t.co/p6a0JD0DMg pic.twitter.com/OPv2UcZGF3
— vitalik.eth (@VitalikButerin) April 9, 2024
The proposal, detailed in a recent analysis, highlights the potential impact of anti-correlation penalties on staking operators and client implementations, shedding light on their role in promoting a more decentralized network.
Economies of Scale and Ethereum Centralization
Currently, stakers benefit from economies of scale, which offer advantages such as enhanced network connectivity, superior hardware reliability, and expert infrastructure management. However, these advantages often lead to centralization, as larger staking operators can leverage their resources to dominate the network.
To address this, mechanisms that counteract the advantages of economies of scale are essential for strengthening decentralization.
Understanding Anti-Correlation Penalties
The concept of anti-correlation penalties, as described by Wahrstätter, is closely linked to the idea of countering the advantages of economies of scale. When a single operator runs multiple validators on one machine and experiences downtime, all validators are affected simultaneously.
This phenomenon results in correlated risks, where the failure of one validator can lead to the failure of others operated by the same entity. Anti-correlation penalties aim to punish those who leverage economies of scale by introducing penalties for correlated risks.
The proposal suggests implementing anti-correlation penalties based on a formula introduced by Vitalik Buterin as reported by Coinspeaker earlier. The formula calculates penalties based on the number of missed attestations compared to a moving average over a specific number of slots. If the number of missed attestations in a slot exceeds the moving average, a correlated penalty is applied. This mechanism targets the hidden connections among validators, aiming to reduce centralization forces.
Impact on Staking Operators and Client Implementations
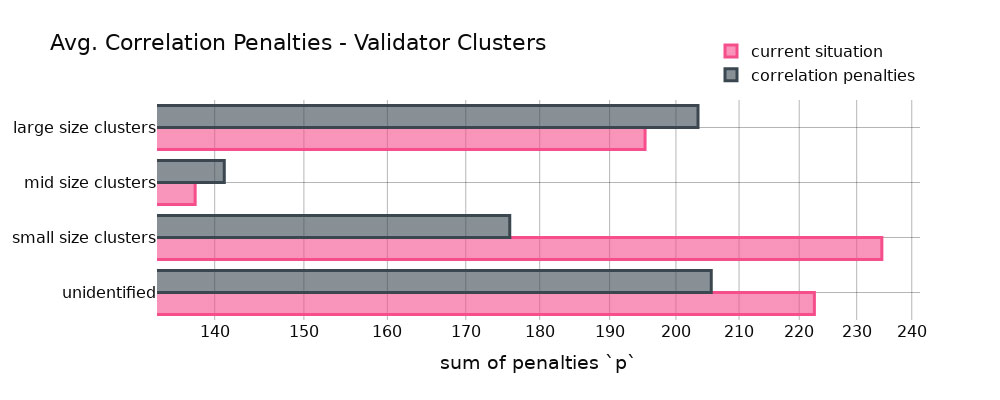
Average Correlation Penalties on Different Validator Clusters. Photo: Ethresear.ch
A quantitative analysis was conducted using a dataset containing all attestations between specific epochs. Wahrstätter analyzed data spanning over 40 days, which included approximately 9.3 billion activities by validators.
The analysis simulated the implementation of Vitalik Buterin’s proposed formula to determine its impact on penalties for staking operators. The results showed that large-size clusters would have higher penalties, while small-size clusters would benefit from reduced penalties.
Similarly, the analysis examined the impact of anti-correlation penalties on client implementations. The results indicated that there would be minor deviations from the current penalty structure, with some clients experiencing slightly higher penalties while others would benefit from reduced penalties.