Some blockchain enthusiasts are too young to remember Microsoft MS-DOS, the cankerous first-generation computing system which laid the foundation for Windows OS, the system that would go on to propel the adoption of personal computing around the world. What was once a difficult task, became a simplified solution that changed the way individuals and companies interacted in a global way.
In much the same way, we are seeing blockchain start-ups, vying to solve the complexity issues associated with accessing blockchain technology. While there is great enthusiasm among CEOs to investigate the potential benefits of blockchain, particularly in big data, the reality is, blockchain is still hugely expensive and overly complicated for the average enterprise to integrate in any practical way.
One company who is hoping to change all that, is Chongqing-based startup NULS. NULS, and their team of fifty employees, are developing a new software system which they say will revolutionize blockchain, making it affordable and accessible for even the smallest of enterprise. This system is called Chain Factory and will be ready for market towards the end of Q4, 2018.
According to Yang Lin, Angel Investor and key code contributor for NULS, “Chain Factory will provide a modular repository containing the basic elements required to build a blockchain without the need to understand complex cryptography.
Developers won’t need to understand blockchain base-level technology in order to achieve their goals because of a more efficient division of labor, between programmers, cryptography specialists and P2P specialists.”
Current Status of Blockchain Creation
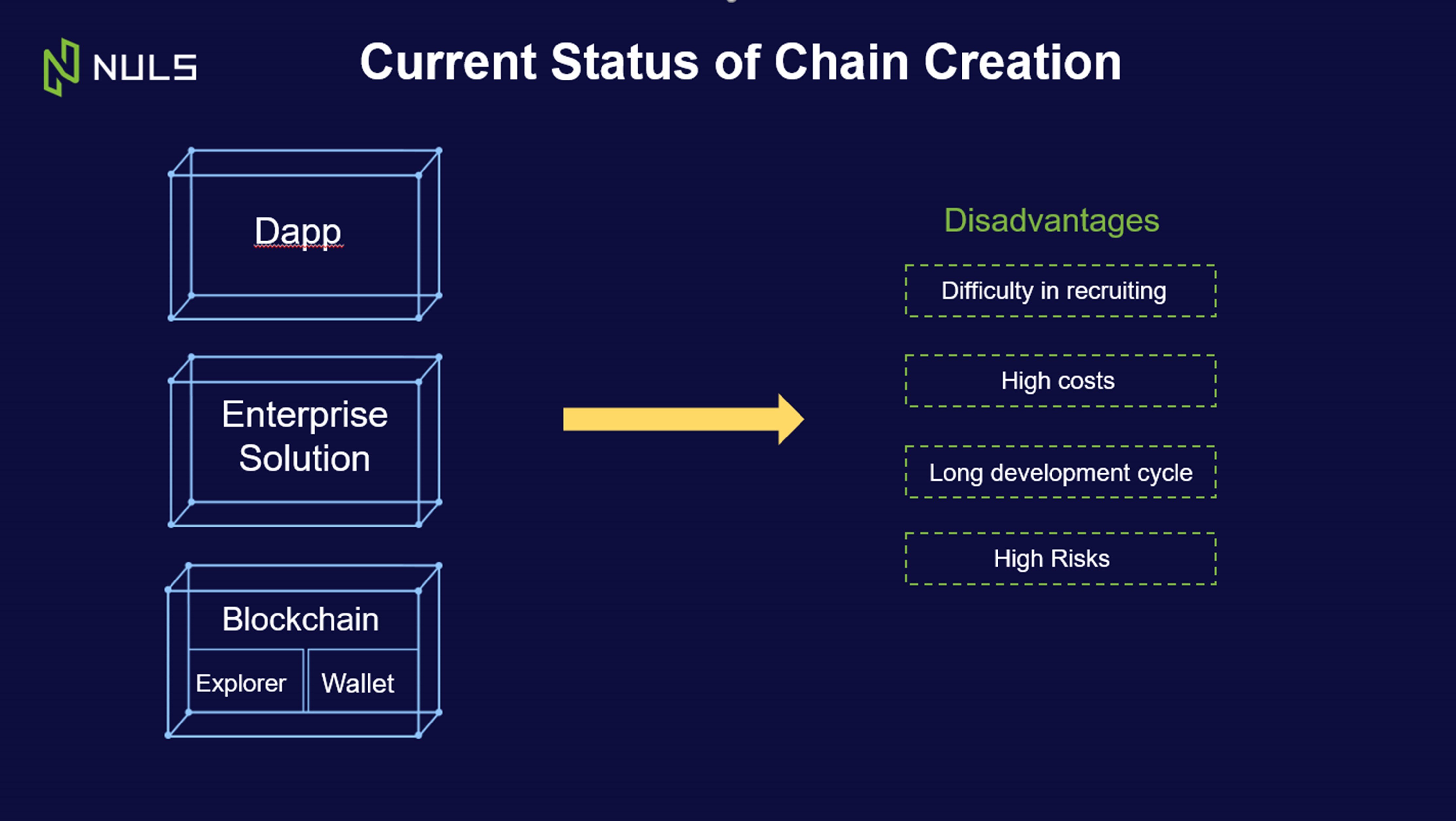
At this point in time, if a company decides to build on the blockchain, they usually start by developing their own blockchain and peripheral products first, such as a wallet and explorer. Then they need to build industry specific applications and eventually a DApp. “It’s a lengthy process”, says Lin, “and fraught with pitfalls along the way.”
These problems include:
- Recruitment difficulties. Good blockchain developers are expensive.
- High costs associated with development.
- Long project development life cycles.
- High risk associated with emerging new technology, including security and interconnectivity.
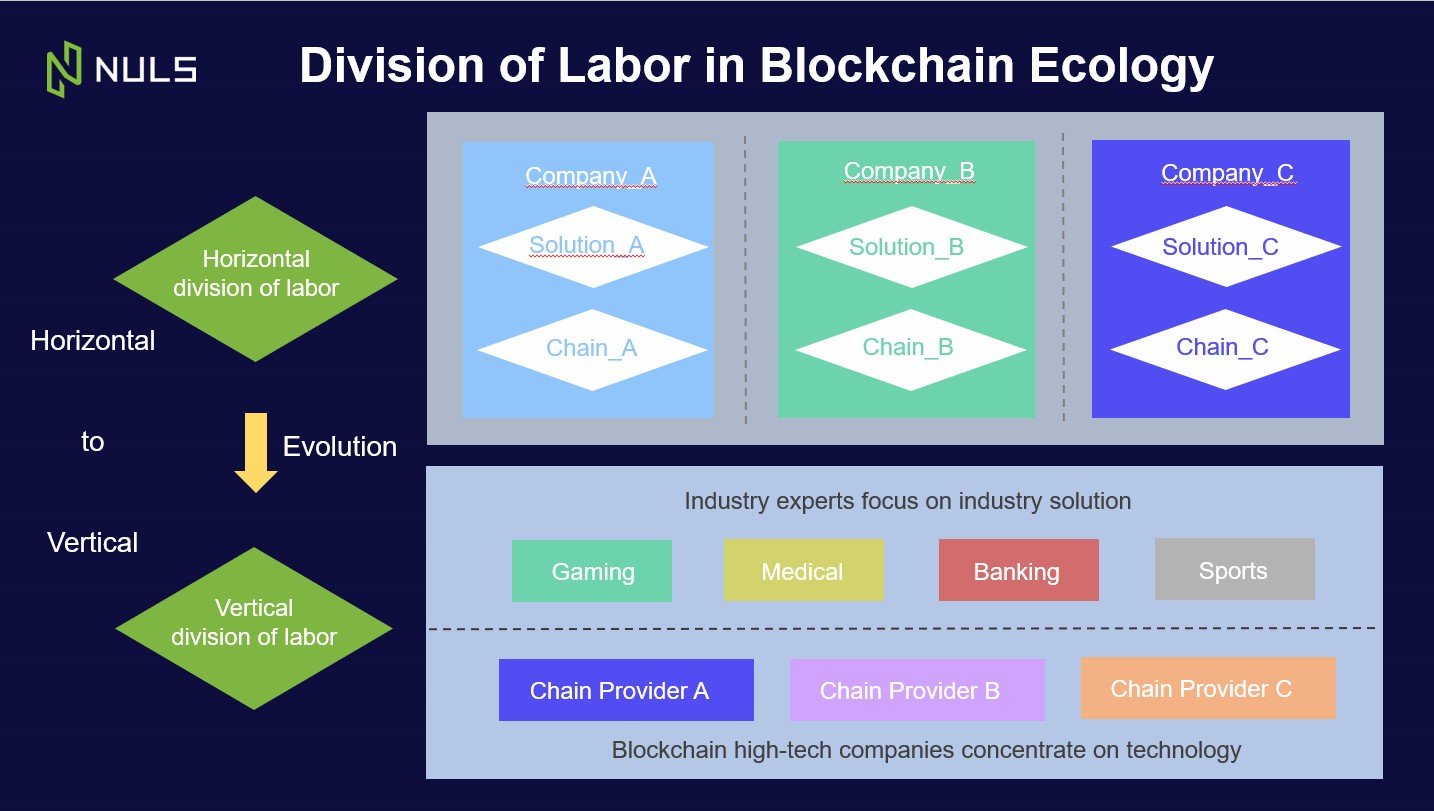
Inevitably, as with the evolution of many industries, the solution to most of these problems will come about through division of labor. “As the market matures,” Lin says, “division of labor is inevitable and will lead to an exponential growth in talent and resources available for blockchain development.”
The movement from horizontal division of labor to vertical, and the specialisation of tasks, is typical in the engineering and accounting industry, and increasingly these days in technology. A vertical matrix offers a higher level of efficiency, through division of resources, skills and expertise.
“Think back to the early days of the internet”, Lin says. “In the ASP era, a programmer undertook the role of database design, as well as website back-end and front-end development. Later, specialized roles came about such as database administer, front-end developer, back-end developer, tester, product manager and UI designer. Similarly, we are seeing the beginning of the vertical division of labor in blockchain.”
Blockchain is giving birth to new base-level positions in such areas as encryption algorithms, consensus algorithms, distributed storage and P2P networks.
Above base-level blockchain, professional positions are emerging in the application layer such as blockchain product manager and DApp business development. According to Lin, “The modular architecture of NULS will undoubtedly help steer the blockchain industry into an era of vertical division of labor.”
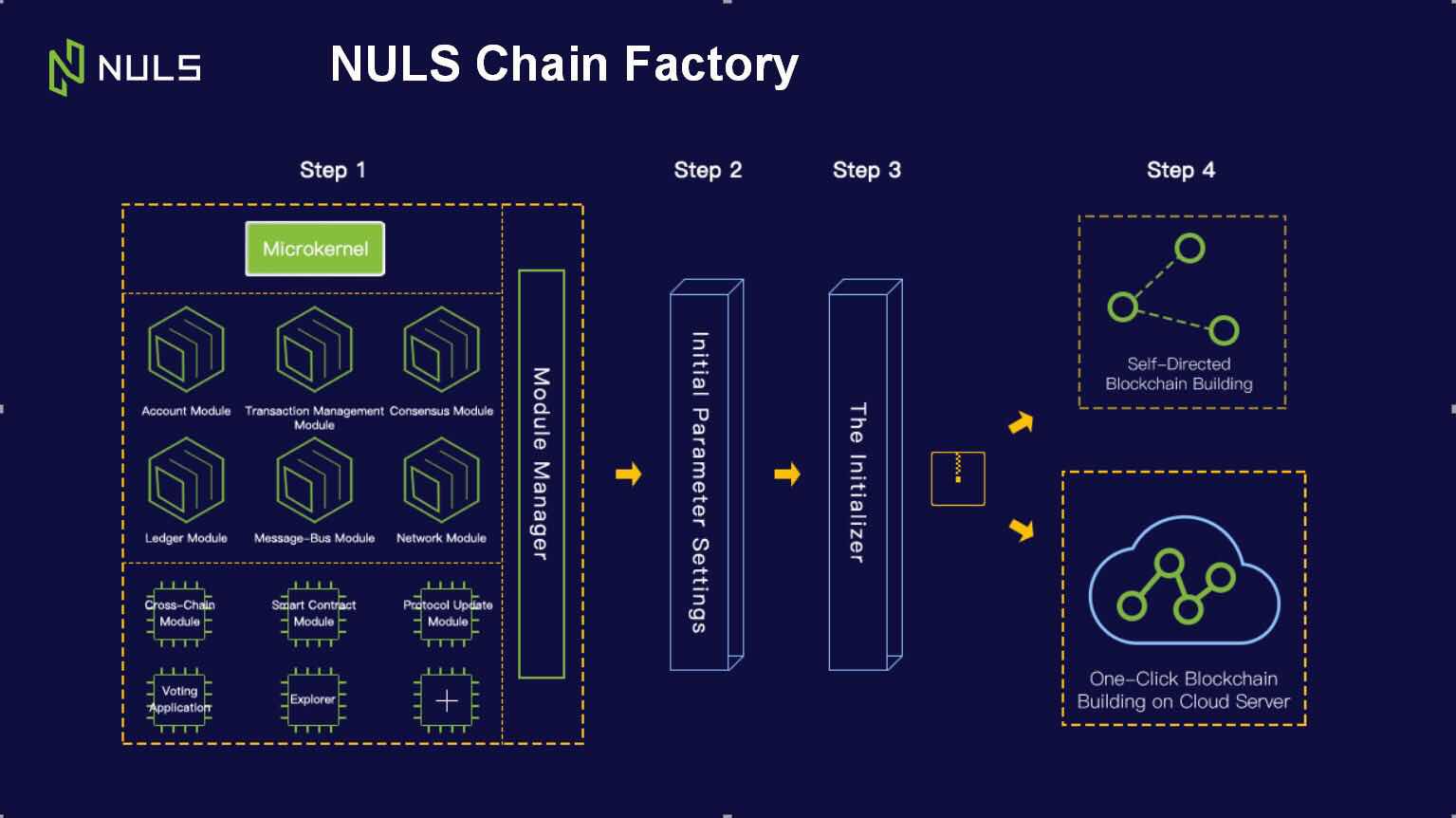
Chain Factory: A Flagship Product
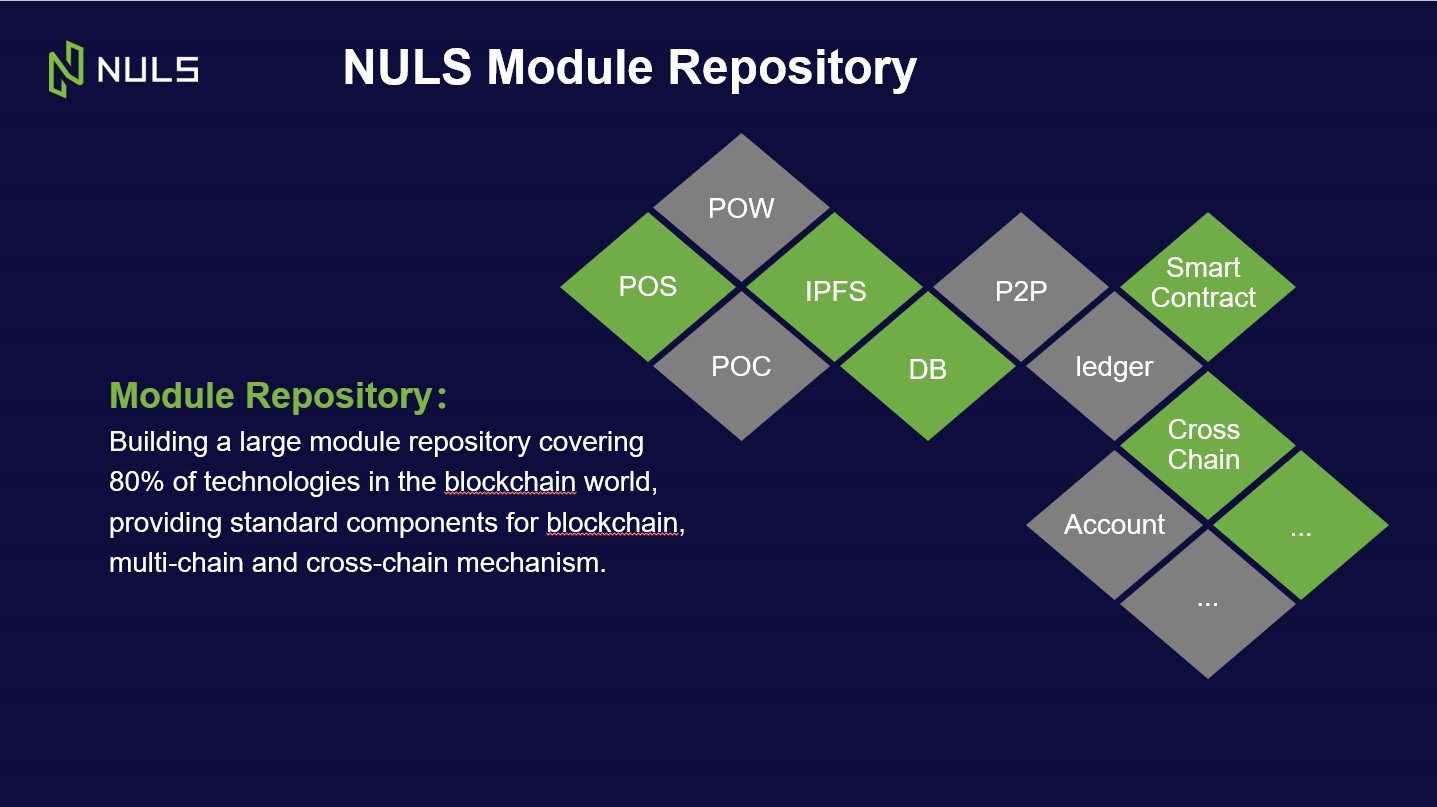
Chain Factory will offer a pluggable modular system, which will launch with all the basic elements required to make a chain. These include microkernel and functional modules such as:
- Ledger
- Accounts
- Consensus
- Network
- Cross-Chain
- Smart contract modules.
According to Lin, “developers won’t need to understand base level blockchain technology. They can build their own customized blockchain by using a simple graphical UI interface.” He continues, “quite quickly, we hope our modular repository will offer plug-and-go solutions to over 80 percent of industries in the blockchain field. Users can customize their chain, public or consortium and set consensus parameters according to their business requirements.”
NULS claim that a developer with little knowledge of base-layer blockchain technology can create their own public chain within minutes (consortium or private chains also possible) using their flagship product Chain Factory.
Assuming the developer understands the parameters of the chain they want to create, such as total number of tokens to be created and consensus mechanism, then it’s just a matter of selecting modules, configuring parameters, downloading an operation package and hey presto – deploy!
Updates, using industry standard cryptography, are synchronized by Chain Factory across the NULS network, which improves system and asset security for everyone in the ecosystem.
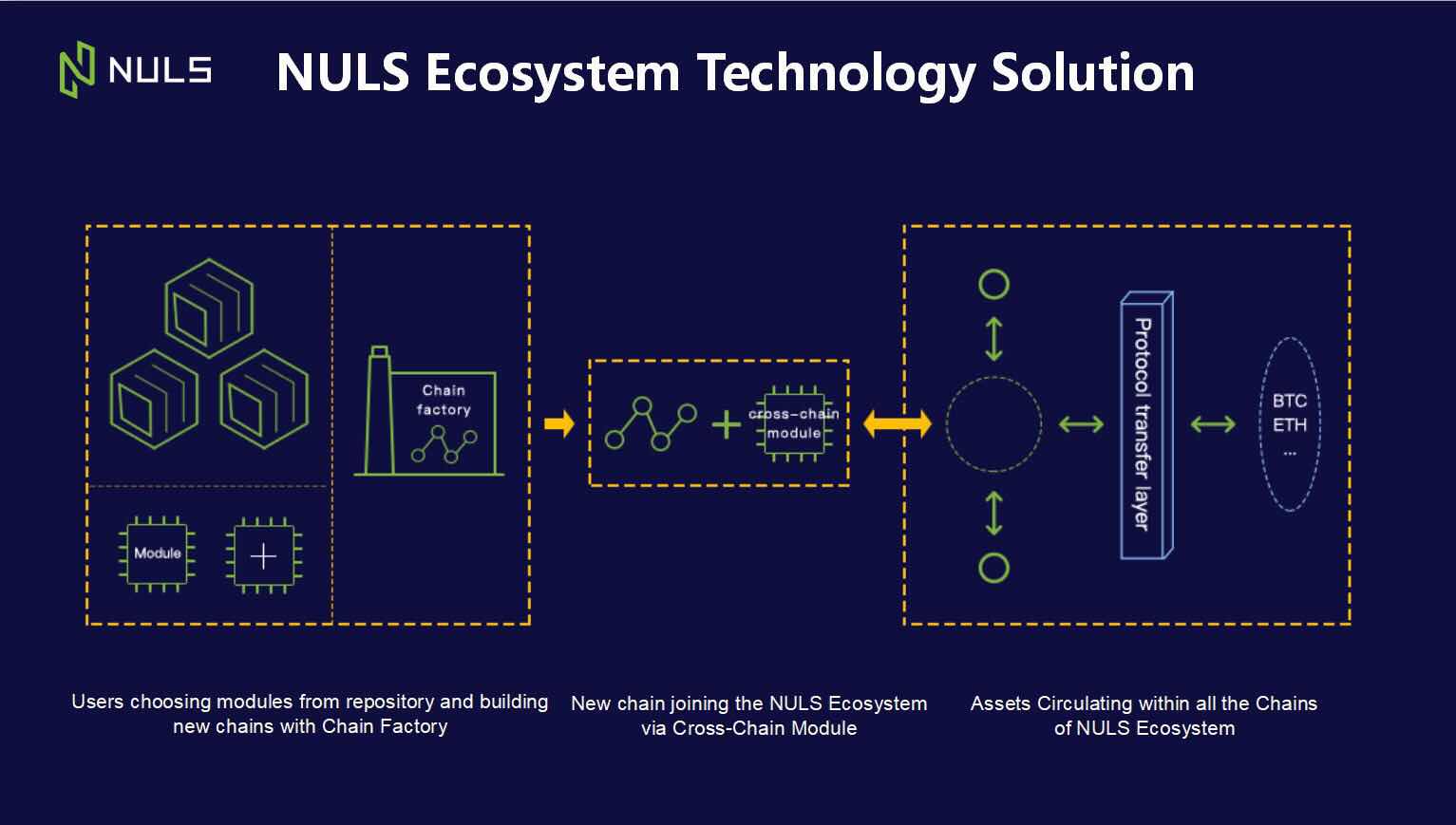
Chain Factory and Cross Chain – Free Flowing Ecosystem
One of the key elements of Chain Factory’s repository kit, is the development of a cross-chain module. Most blockchain systems are built on a single, isolated ecosystem, so assets and information cannot be transmitted across different blockchains. It is a like a shop only accepting cash because it does not have the technology to connect with a third party like Visa. It is easy to see how this would greatly limit the potential of enterprise to conduct business. It is the same with blockchain- and that, is where cross-chain technology comes in.
Cross-chain technology is still in its relative infancy, but NULS are working on delivering a solution as part of their Chain Factory offering.
Cross-chain provides a secure means to connect with other chains in a platform ecosystem, allowing interoperability and scalability without the need to compromise on privacy and security. Interoperability will be the key driving force behind the growth of the NULS ecosystem, because it allows for the free circulation of assets and value from chain to chain.
Think of cross-chain like a bridge, connecting enterprises economically and socially. It provides a means for data transfer, allowing companies to collaborate and grow together instead of competing for market share. Innovations can spread quickly from chain to chain, resulting in a truly global enterprise ecosystem which benefits all those who participate in the network. It should also widen the scope for cryptocurrency usability.
At a basic level, chains will link to a central satellite chain, which organizes the cross communication. Details of asset transfer from one chain to another will be stored in the satellite chain, ensuring accountability and security. The aim is to allow the transfer and free circulation of digital assets within an entire ecosystem.
Chains which originate outside of the NULS ecosystem, for example Ethereum, Bitcoin Cash or Bitcoin, will be able to join the system by means of a special mechanism which allows for a unified protocol. In fact, Lin says “we have been collaborating with BCH and other projects to develop joint cross-chain solutions.”
Speaking at a NULS conference in Seoul, Korea this week, Lin said “We have moved from a single module to a module repository, and from module repository to Chain Factory. What we are proposing is a solution for a complete cross-chain value ecosystem. Although I think with a developer’s mind, I do believe that the world needs blockchain and will understand it’s true economic and social value in years to come.”
As blockchain evolves, so too will the solutions which fire this technology revolution. According to Wintergreen Research’s report “The Blockchain Market Shares, Strategy and Forecast 2018-2024″, the global market for blockchain in 2017 was $708 million and is expected to reach $60.7 billion by 2024.
This growth will happen as blockchain proves it value by managing digital transactions across enterprises and encouraging business collaborations in a speedy and cost-effective manner. The race to create a new digital economic structure has begun.